Deployment and Instance Management
This section is all around how to deploy and manage code, applications, and machines
Elastic Beanstalk
- Elastic Beanstalk is a developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
- Helpful for porting on-prem to cloud with minimal changes
- If you can dockerize your container, you can deploy on Beanstalk
- Beanstalk meant to "replatform" apps
- Supports many platforms: Go, Java w/ Tomcat, Python, Node.js, anything Dockerized really, etc...
- It's basically just a wrapper around a number of other services, and it's all displayed in one view
- Beanstalk is free, but you pay for underlying infra
- Management:
- Instance config, OS, and general deployment compute hadled by beanstalk
- App code is responsibility of developer
- Three architecture mdoels:
- Single instance deployment is good for dev
- LB + ASG good for prod / pre-prod web apps
- ASG good for non web-apps (workers, backend services, etc)
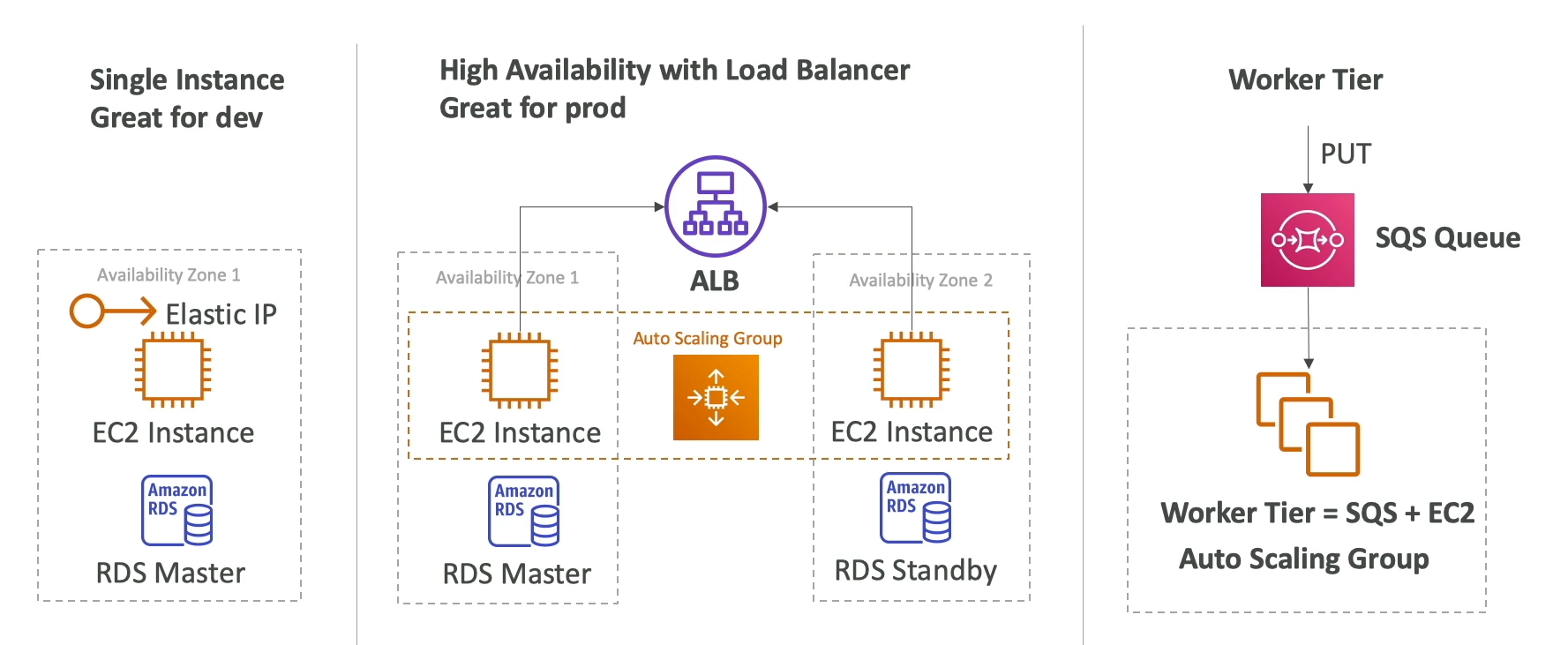
- Web Server vs Worker:
- Any decoupling ==== SQS!!!
- App performs long running tasks to complete, then offloadnig them to dedicated workers is typically used
- Decoupled beanstalk can help us manage web app and worker environment
- Blue / Green Deployment
- Can use a new environment (green) and validate independently
- Use Route53 weighted routing to redirect small amounts of tradffic to Green, and shift over time
- Beanstalk "Swap URLS" DNS Swap feature
Code Deploy
- Helps us to Deploy code!
- Deploy new versions of code to EC2, Docker containers on ECS, etc...
- Ansible, Terraform, Chef, Puppet, etc... are useful, but can use AWS CodeDeploy out of the box with EC2, ECS, ASG, and Lambda
- Does in-place update of fleet of EC2 instances
- Can use hook to verify the deployment after each deployment phase
- CodeDeploy fulls manages take down, in place updaets, and having V2 rolled out on EC2's
- EC2 Update types:
- In-place updates:
- Updates current EC2 instances
- Instances newly created by ASG will automatically get automated deployment
- Blue/Green deployment
- New ASG is created for V2, and new launch templates are used
- CHoose how long we keep old instances
- Start routing traffic to V2
- Requires ELB
- CodeDeploy will slowly remove old instances and keep new ones
- In-place updates:
- CodeDeploy to Lambda
- Traffic shifting feature
- Pre and Post traffic hooks to validate deployments
- These are just more lambda functions to run before and after deploying new code
- Easy and automated rollback using CWatch Alarms
- CodeDeploy can rollback if CWatch alarms go over threshold
- SAM framework natively uses CodeDeploy
- CodeDepoy to ECS
- Support B/G deployment on ECS and Fargate
- Setup is done on ECS Service definition, not on CodeDeploy UI
- New task set is created and traffic gets rerouted to new task set
- If everything is good for X minutes the old task set is terminated
- Supports Canary deployment
10Percent5Minutes - CodeDeploy just ensures that ECS Task definitions get shifted over time, and then ensures stability
CloudFormation
- Brings IaC into AWS
- Helps to port across accounts and regions
- Backbone of:
- Beanstalk
- Service Catalog
- SAM (Serverless App Model)
- Retain data on deletes
- DeletionPolicy
- Can use on any resource to control what happens when a template is deleted
- Retain
- Specifies a resource to preserve upon deletion
- Snapshot
- EBS, RDS, ElastiCache, Redshift, DBCluster, etc
- Delete
- Same as above, but for S3 you need to delete everything inside of it first
- DeletionPolicy
- CustomResources
- Can define a custom resource to address any challenges from native CF
- Backed by lambda function to CRUD resources
- Empty S3, Get AMI, etc!
- StackSets
- CRUD stacks across multiple accounts and regions
- Basically a module
- Admin to create stack sets
- Updating a stack set means updating all instances from there, throughout all accounts and regions
- Enable AutomaticDeployment feature to auto deploy to accounts in AWS Orgs or OU's
- Drift
- What happens if someone manually alters the resources?
- CF Drift compares all resources to state file
- Can be done on entire stacks, or an individual stack
- Secrets Manager
- Can set and use secretsin CF natively
- Can help us ensure that whenever a secret rotates, the value sitting in other resources such as RDS will automatically update
- Can handle imports into individual, or entire stacks
- Need to create a template that describes the entire stack including currently tracked resources, and newly desired imported resources
AWS Service Catalog
- For users new to AWS who have too many options
- Allows users to access a self-service portal with authorized access
- Bascially allows users to see pre-authorized resources defined by admins, and then helps them to deploy apps using those resources
- Admins use CloudFormation templates to create stacks which are approved stacks!
- Allows IAM perms to access the stacks
- Users can then launch the products with variable naming abilities
- Stacks assigned to portfolios (teams)
- Teams are presented a serlf-service portal to launch products
- All deployed products are centrally managed
- Helps w/ governance, compliance, and security
- Integrates with 3rd party portals like ServiceNow
Serverless Application Model (SAM)
- Framework for developing and delpoying serverless apps
- All configs are done via YAML code
- Lambda, DynamoDB, API GW, Step Functions, etc
- SAM can use CodeDeploy to deploy lambda functions
- Uses CFormation on backend to deploy
- CICD Arch
- CodePipeline for DevOps CICD
- CodeCommit for git style version control
- CodeBuild for build, test, package
- CloudFormation + SAM for sending to CodeDeploy
- CodeDeploy helps to shift traffic on lambdas
- CodePipeline for DevOps CICD
- Just need to remember SAM uses CodeDEploy on backend for lambdas
AWS CDK
- Cloud Development Kit
- Define clodu infra using familiar language (Python, JS, Java, etc..)
- When you don't want to use CF directly with YAML
- After writing CDK it will compile into CFormation YAML
- Allows for for loops, file access, and other things that YAML can't handle
AWS SSM
- Helps to manage cloud and on-prem VM's
- Need to install SSM agent, or use AMI with it pre-installed
- Installed by default on AWS Linux AMI + some Ubuntu AMI
- Works for Windows and Linux
- If an instance can't be controlled with Systems Manager, it's probably an issue with the agent
- What can SSM do?
- Allows us to run commands over One:Many instances
- Allows for scripting and updating of hundreds of instances across cloud and on-prem
- Integrated with IAM and CloudTrail
- No need for SSH!
- Rate Control (how fast to run over instances) + Error control (what to do on failure)
- SSM agent ensures all of this can be done on the machine from calling party
- Common use cases:
- Send command before an ASG instance is terminated
- Can allow some lifecycle hook to run before an EC2 instance is terminated / deleted
- When EC2 goes into
Terminating:Waitstate, it will notify EventBridge which can call SSM Automation on the EC2 instance itself to run some final commands before shutting downSendCommandis sending a command to the EC2 instance
- At this point our Lifecycle Hook can shut the instance down
- Send command before an ASG instance is terminated
- Patch Managers
- Helps
- Define a Patch Baseline to use (or multiple if needed)
- Define Patch Groups:
- Can define based on:
- Tags
- Name
- Region
- etc
- Can define based on:
- Define Maintenance Window for schedule duration, registered groups, and registered tasks
- Run
AWS-RunPatchBaselineRun Command which runs on Windows and Linux- Rate Control: How many instances to run at a time - concurrency and parallelism
- Error Control: What to do on errors
- Monitor Patch Compliance using SSM Inventory
- Session Manager
- Allows for secure shell to EC2 and on-prem without opening port 22 and using SSH keys
- Can just use UI based shell where Systems Manager is taking care of connecting and authentication
- All commands logged and can be sent to S3 or CloudWatch
- Can use CloudTrail to see
StartSessionevents
- OpsCenter
- Resolve Operational Issues (OpsItems) related to AWS resources
- Issues, Items, and Alerts
- Aggregates information to resolve issues on each OpsItem such as:
- AWS Config changes and relationships
- CloudTrail Log
- CloudWatch Metrics
- CloudFormation Stack info
- Across all these groups we can use Automation Runbooks via SSM Runbook Automations to resolve the incidents
- EventBridge and CloudWatch Alarms can create OpsItem events
- Resolve Operational Issues (OpsItems) related to AWS resources
AWS Cloud Map
- Fully managed resource discovery service
- Helps with service discovery / DNS routing + redeployment
- Moving from V1 to V2 of a backend service from a frontend service
- Creates a map of your backend services / resources that app depends on
- You register your application components, their locations, attributes, and health to AWS CloudMap
- Acts as a ZooKeeper-esque service discovery mechanism and helper
- Integrations with Health Checking to stop sending traffic to unhealthy endpoints